Non-destructive testing (NDT) is a group of analysis techniques used to evaluate the properties of materials, components, or systems without causing damage. It aims to detect flaws, irregularities, or changes in material properties that could lead to failure. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, and dye penetrant testing. These techniques are widely used in industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, and construction to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with standards, while preserving the integrity of the tested items.
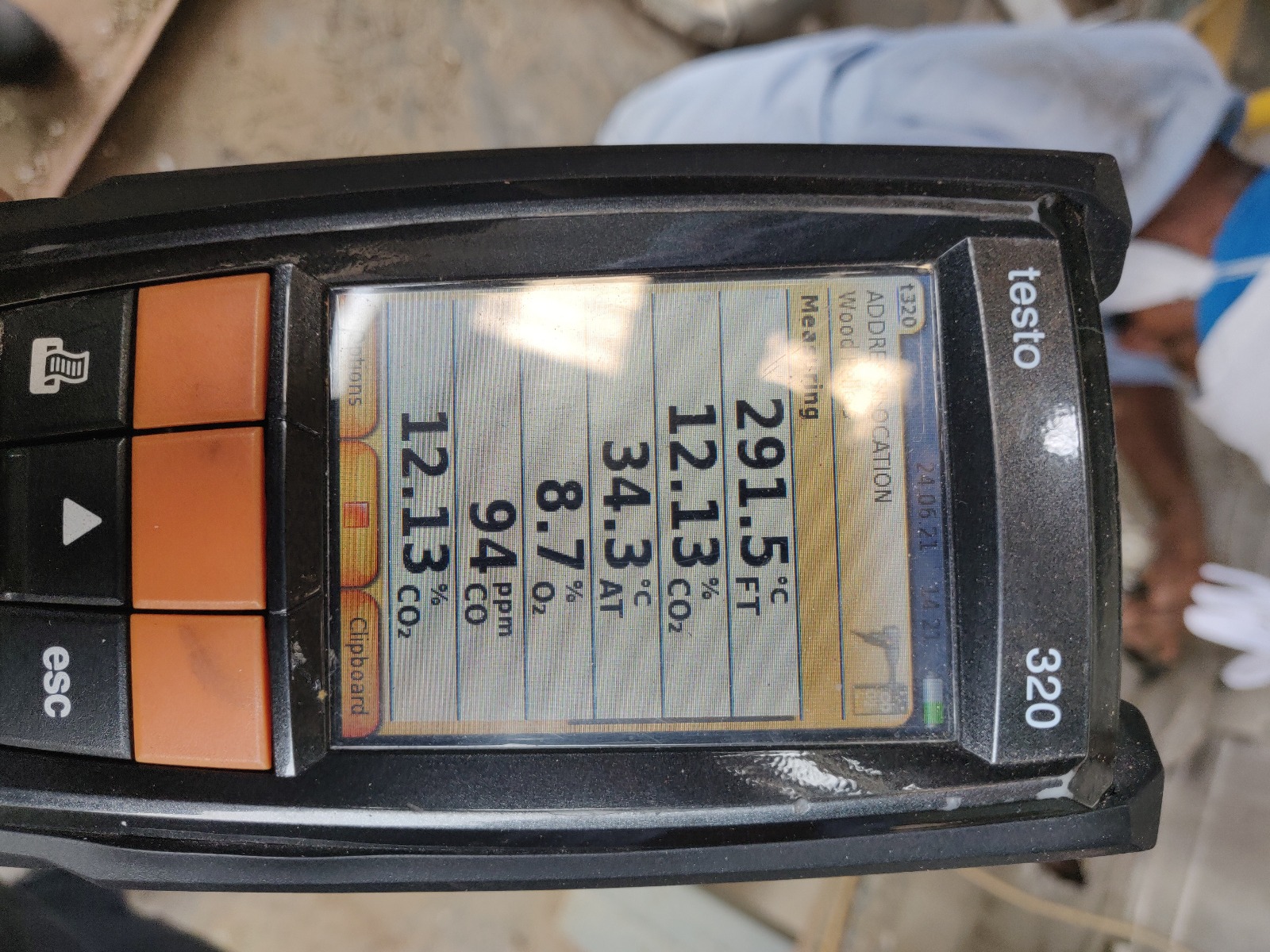
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws, measure thickness, and characterize materials without causing damage, ensuring structural integrity in various industries. Ultrasonic Flaw Detection (A-Scan) is a technique using ultrasonic waves to identify and locate internal defects or flaws within materials by analyzing the time taken for sound wave reflections and Ultrasonic Oxide Thickness Measurement uses high-frequency sound waves to non-destructively measure oxide layer thickness, ensuring material integrity and preventing corrosion.
Enquire NowMagnetic Particle Testing Yoke (MT)
using the Yoke method involves placing a portable magnetic yoke, which can be an electromagnet or a permanent magnet, on the surface of the material to be inspected. The yoke induces a magnetic field in the area between its poles. Ferrous particles, either dry or suspended in a liquid, are then applied to the surface. These particles accumulate at any surface or near-surface discontinuities, like cracks, due to magnetic flux leakage, forming visible indications. The Yoke method is versatile, suitable for various shapes and sizes of ferromagnetic materials.
Enquire Now

Eddy Current Testing (ET)
It utilizes electromagnetic induction by passing alternating current through a coil, creating eddy currents in the material. Disturbances in the material, like cracks or defects, alter eddy current flow, which is detected by measuring changes in the coil's impedance or phase. ET is valuable for flaw detection in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
Enquire NowNatural Frequency Test (NFT)
is a non-destructive testing method that evaluates the structural integrity of materials by exciting them with an external force and measuring their response frequency. It helps detect changes in material properties, stress, or fatigue, aiding in assessing structural health and predicting potential failures in engineering components like bridges and buildings.
Enquire Now
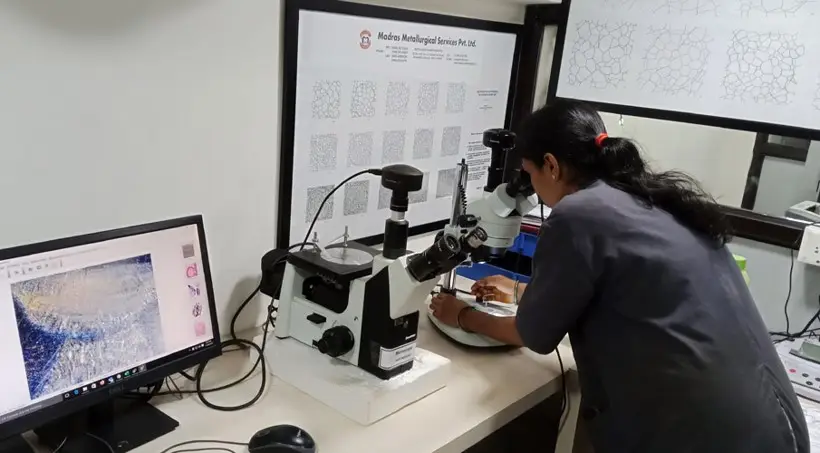

In-situ Metallography
also known as Replica Metallography, is a non-destructive testing technique used to examine the microstructure of materials in their operating environment. A replica of the surface is created by making an impression with a special material or compound. This replica is then examined under a microscope to analyze features such as grain structure, inclusion content, and defects, providing valuable insights into material properties without the need for sample removal.
Enquire NowFibroscopy / Endoscopy (Internal Inspection of Headers)
Fibroscopy, also known as Endoscopy, is a method for internally inspecting headers or other components. A flexible fiberoptic probe with a camera and light source is inserted into the header, allowing visual examination of the internal surfaces and structures. This technique enables detection of defects, corrosion, deposits, or other issues without the need for disassembly, facilitating timely maintenance or repairs to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Enquire Now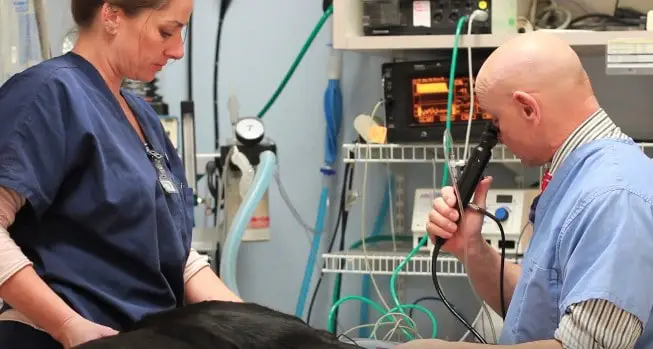
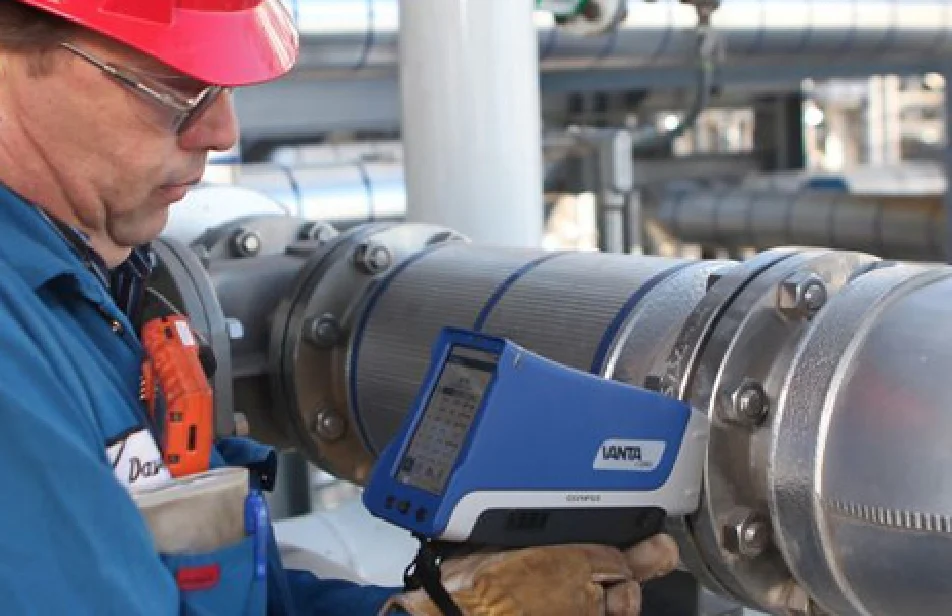

Parent Metal Identification (PMI)
is a method used to verify the chemical composition of a metal component or structure. It involves analyzing a small sample to determine its elemental composition and compare it to the expected composition of the parent metal. PMI ensures that the correct materials are used in construction or manufacturing processes, preventing material mix-ups, ensuring compliance with specifications, and maintaining the integrity and safety of the final product or structure.
Enquire NowHardness testing
is a method used to determine the resistance of a material to indentation or scratching. Various techniques, such as Rockwell, Brinell, and Vickers, are employed to measure hardness, providing insights into material properties like strength, wear resistance, and ductility. It finds applications in quality control, material selection, and assessing heat treatment effects in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and metallurgy to ensure product reliability and performance.
Enquire Now
Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT)
is a method used to detect surface-breaking defects in materials. It involves applying a penetrating liquid dye onto the surface of the test object, allowing it to seep into any surface discontinuities through capillary action. After excess dye is removed, a developer is applied to draw out the trapped dye, revealing the presence of defects like cracks, porosity, or leaks. DPT is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
Enquire NowRadiography
in Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) uses X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of materials. The radiation penetrates the material and is captured on a detector or film placed on the opposite side. Differences in material density and internal features create a detailed image, revealing flaws like cracks, voids, or inclusions. This method is highly effective for inspecting welds, castings, and complex assemblies without damaging the components. Radiography ensures the integrity and quality of critical parts in various industries.
Enquire Now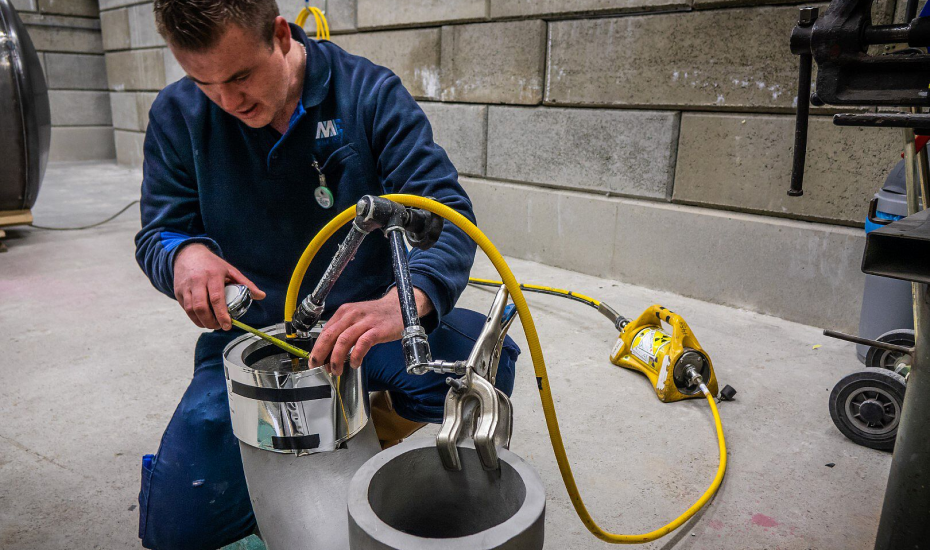
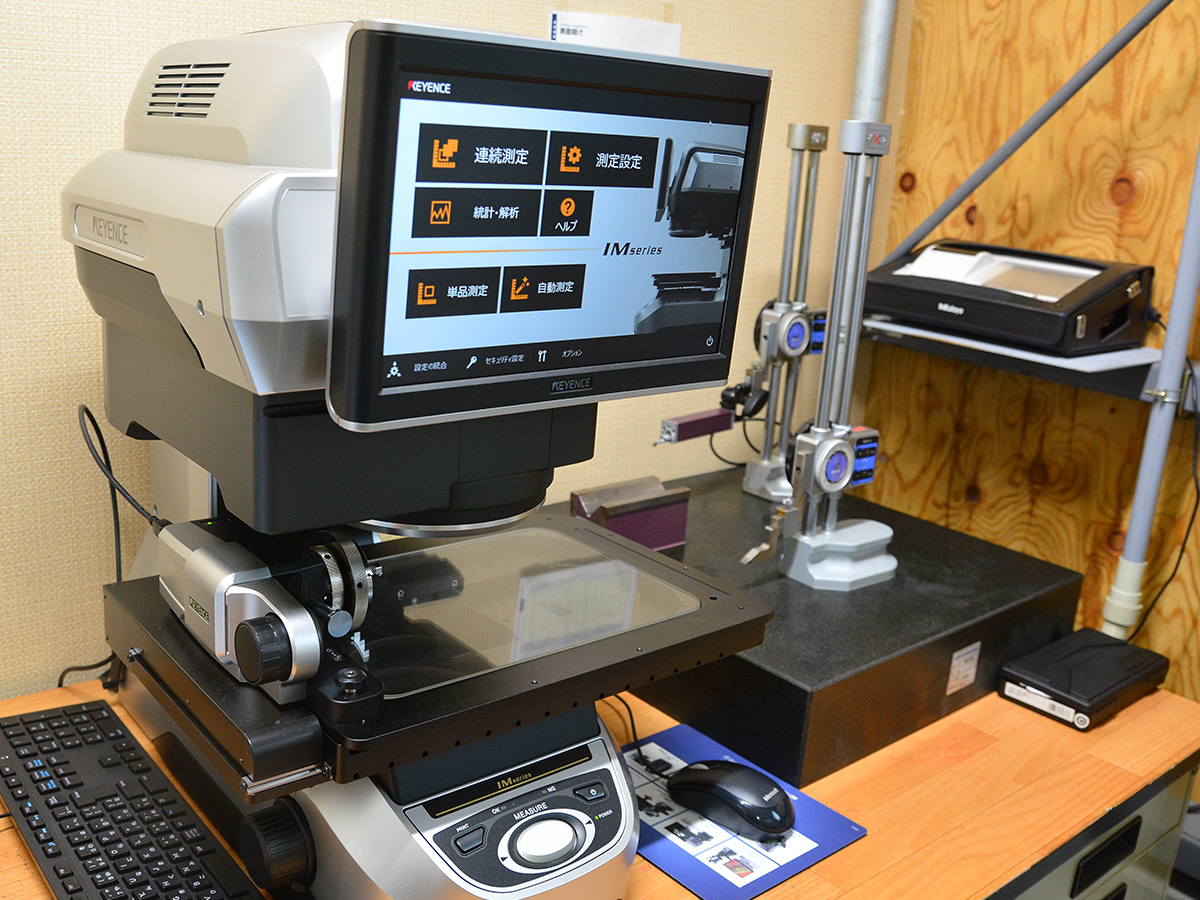

Dimension measurement
in involves assessing the size and geometry of components without causing damage. Techniques such as ultrasonic thickness gauging, laser scanning, and optical measurement systems are used. These methods provide precise measurements of dimensions, thickness, and surface profiles. Accurate dimension measurement ensures components meet specifications and tolerances, crucial for quality control and performance. This process is vital in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where precision and reliability are paramount for safety and functionality.
Enquire NowStress relieving (Pre-Heating Post Heating)
Stress relieving in involves controlled heating and cooling processes to reduce residual stresses in materials, enhancing their structural integrity. Pre-heating gradually warms the material before welding or processing, minimizing thermal shock and distortion. Post-heating, or post-weld heat treatment (PWHT), uniformly reheats the material after welding to alleviate stresses induced during fabrication. These techniques prevent cracking, improve mechanical properties, and ensure the material's stability and performance, crucial for high-stress applications in industries like construction, aerospace, and petrochemical.
Enquire Now
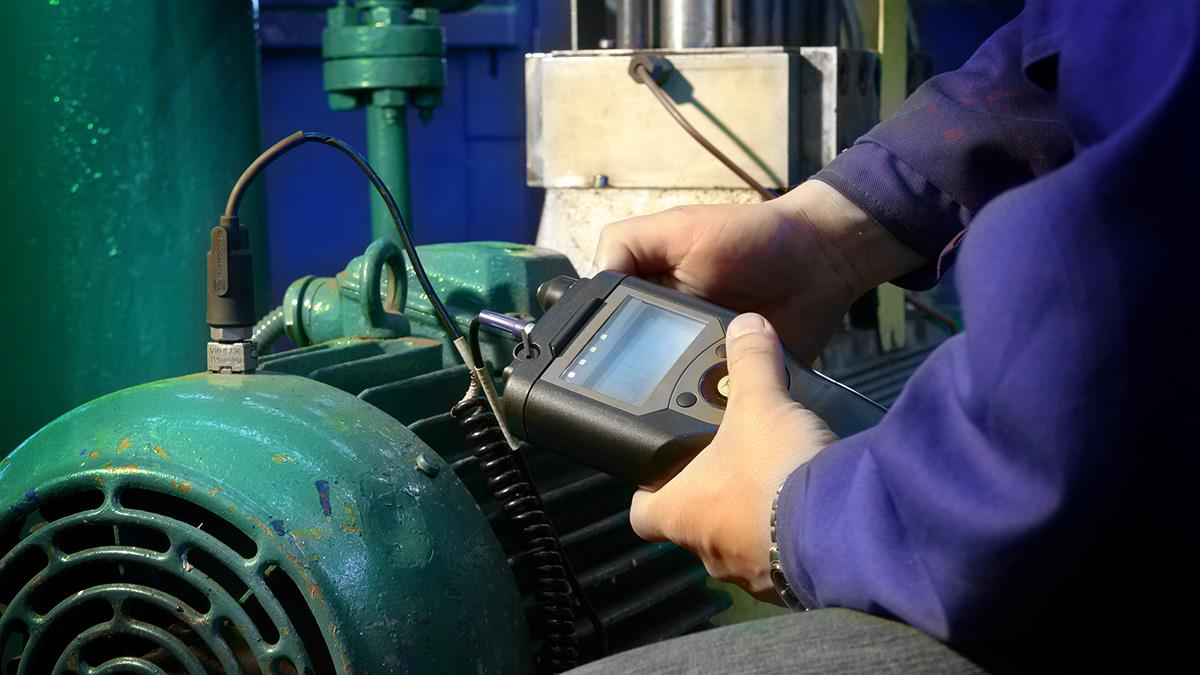

Vibration Analysis
in Non-Destructive Testing involves monitoring and analyzing the vibrational patterns of machinery and structures to detect anomalies and potential failures. Sensors measure vibrations, and data is analyzed to identify imbalances, misalignments, or wear in components. This technique helps in early detection of issues, preventing costly breakdowns and extending equipment life. Vibration analysis is essential in maintaining the reliability and safety of rotating machinery, such as motors, turbines, and pumps, in industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and energy.
Enquire NowNoise Analysis
in involves monitoring and interpreting sound emissions from machinery and structures to identify defects or irregularities. Specialized sensors and microphones capture noise data, which is then analyzed to detect anomalies such as leaks, cracks, or mechanical faults. This method allows for early identification of issues, enhancing maintenance and preventing failures. Noise analysis is particularly useful in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where ensuring the reliability and safety of equipment is critical
Enquire Now

Structure Stability Test
in NDT assesses the integrity and durability of a structure under various loads and conditions. Techniques like static load testing, dynamic analysis, and vibration monitoring are employed to evaluate how a structure responds to stress, strain, and environmental factors. The goal is to identify weaknesses, ensure compliance with safety standards, and predict the structure's performance over time. This testing is crucial in construction, civil engineering, and infrastructure maintenance to ensure the safety and longevity of buildings, bridges, and other critical structures.
Enquire NowThickness measurement
using Ultrasonic Testing (UT-T) is a precise, non-destructive method for determining material thickness. An ultrasonic transducer sends high-frequency sound waves into the material, and the time it takes for the echoes to return is measured. This data is used to calculate the thickness. UT-T is effective for detecting corrosion, erosion, and wear in metals, plastics, and composites. It is widely used in industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and petrochemicals to ensure material integrity and compliance with safety standards.
Enquire Now
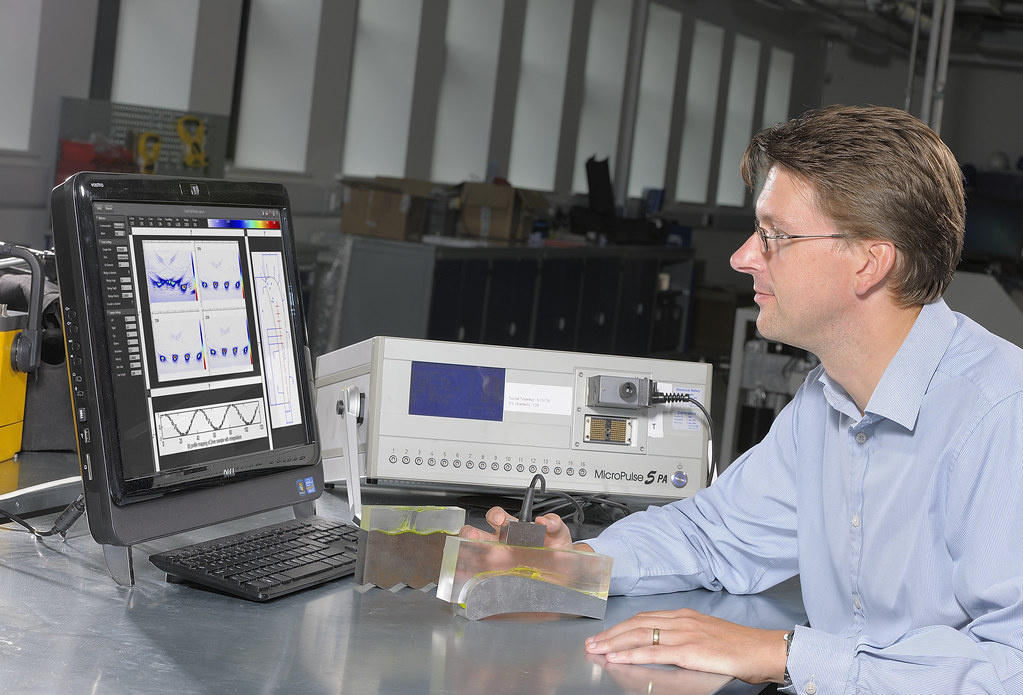

Advance Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT)
Advanced Ultrasonic Testing, specifically Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT), utilizes multiple ultrasonic elements in a single probe to generate and receive sound waves. These elements can be individually controlled to adjust beam angle, focus, and direction, allowing for precise inspection of complex geometries and materials. PAUT provides detailed imaging of internal structures, such as welds, and offers improved flaw detection and sizing capabilities compared to conventional ultrasonic methods. It is widely employed in aerospace, automotive, and energy industries for quality assurance and safety assessments.
Enquire NowOxide Scale
In-situ oxide scale measurement involves assessing the thickness and composition of oxide layers both inside and outside a material. This is typically done using techniques like optical microscopy, electron microscopy, or spectroscopy. By analyzing these layers, engineers can evaluate material degradation, corrosion rates, and overall integrity, crucial for ensuring the reliability and lifespan of components in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and manufacturing.
Enquire Now

Core Cutting
is a method used to extract cylindrical samples, or cores, from materials such as concrete, rock, or metal. This process involves drilling or cutting into the material to remove a cylindrical section for analysis or testing. Cores provide insights into the material's properties, such as strength, composition, and integrity, allowing engineers and researchers to assess its suitability for various applications. Core cutting is commonly used in construction, geology, materials science, and civil engineering for quality control and research purposes.
Enquire Now

